India is a vibrant tapestry of cultures, religions, and traditions, and the Muslim population in India forms an integral part of this diverse nation. With over 200 million Muslims, India boasts the third-largest Muslim population in the world, after Indonesia and Pakistan. This community has played a pivotal role in shaping the country’s history, culture, and socio-economic landscape. From the Mughal era to modern-day India, the Muslim population has contributed significantly to art, architecture, cuisine, and governance, making their presence felt in every sphere of life.
The Muslim population in India is not just a religious minority but a dynamic and diverse group with unique traditions and practices. Spread across various states, the community exhibits a wide range of cultural and linguistic diversity. While states like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal have large Muslim populations, regions like Kerala and Kashmir also showcase distinct Islamic influences. This diversity enriches India’s pluralistic identity and fosters mutual respect among communities.
Despite facing challenges such as socio-economic disparities and political tensions, the Muslim population in India continues to thrive and contribute to the nation’s progress. Their resilience and adaptability are evident in their achievements in education, entrepreneurship, and public service. Understanding the Muslim population in India is crucial to appreciating the country’s multicultural ethos and fostering harmony in a rapidly changing world.
Read also:Understanding Vasozyte A Comprehensive Guide To Its Role And Benefits
Table of Contents
- A Historical Perspective: How Did the Muslim Population in India Emerge?
- Demographics and Distribution: Where Do Muslims Live in India?
- Cultural Contributions: What Role Has the Muslim Population Played in Shaping Indian Heritage?
- Economic Impact: How Does the Muslim Population Contribute to India’s Economy?
- What Challenges Does the Muslim Population in India Face Today?
- Political Influence: How Does the Muslim Vote Shape Indian Democracy?
- Social Initiatives: Are There Efforts to Empower the Muslim Community in India?
- What Does the Future Hold for the Muslim Population in India?
A Historical Perspective: How Did the Muslim Population in India Emerge?
The origins of the Muslim population in India can be traced back to the early medieval period when Islamic influences began to permeate the subcontinent. The first significant interaction occurred during the Arab conquest of Sindh in 712 CE, led by Muhammad bin Qasim. However, it was the Delhi Sultanate (1206–1526) and the Mughal Empire (1526–1857) that cemented Islam’s place in Indian history. These empires not only brought administrative reforms but also introduced Persian culture, art, and architecture, which left an indelible mark on Indian society.
The Mughal era, in particular, is celebrated for its contributions to India’s cultural heritage. Iconic structures like the Taj Mahal, Jama Masjid, and Red Fort stand as testaments to the architectural brilliance of the time. Moreover, the Mughals fostered an environment of intellectual exchange, blending Islamic and Indian traditions. This period saw the flourishing of Urdu literature, miniature paintings, and classical music, which continue to be cherished today.
Post-independence, the Muslim population in India faced a turning point. The partition of British India in 1947 led to the creation of Pakistan and Bangladesh, resulting in large-scale migration and communal tensions. Despite these challenges, Muslims in India chose to remain and contribute to the nation-building process. Today, their history is a testament to their resilience and adaptability in the face of adversity.
Demographics and Distribution: Where Do Muslims Live in India?
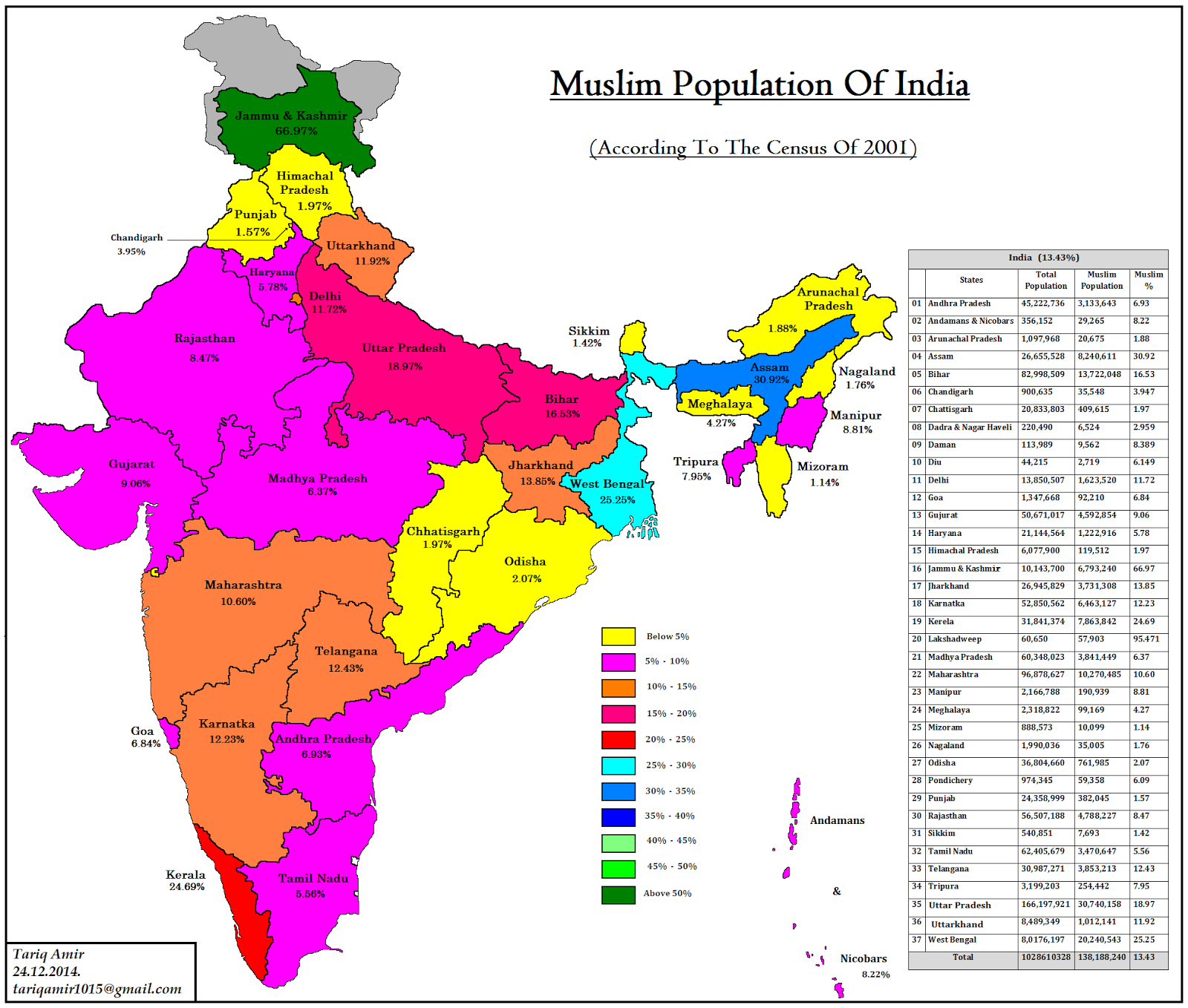
The Muslim population in India is geographically diverse, with significant concentrations in specific states and regions. According to the 2011 Census, Muslims constitute approximately 14.2% of India’s total population, making them the largest religious minority in the country. Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal are home to the largest Muslim populations, while states like Kerala and Jammu & Kashmir also have substantial Muslim communities.
Here are some key insights into their distribution:
- Uttar Pradesh: With over 40 million Muslims, it has the highest Muslim population in India.
- West Bengal: Known for its syncretic culture, the state has a significant Muslim presence, particularly in districts like Murshidabad and Malda.
- Kerala: The Muslim community here is known for its high literacy rates and entrepreneurial spirit.
- Jammu & Kashmir: Muslims form the majority in the Kashmir Valley, contributing to the region’s distinct identity.
This geographic diversity is mirrored in the community’s linguistic and cultural practices. For instance, Muslims in Kerala speak Malayalam, while those in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar predominantly speak Urdu or Hindi. Such regional variations highlight the adaptability of the Muslim population in India and their integration into local cultures.
Read also:Ct Wife The Challenge A Journey Of Resilience And Triumph
Cultural Contributions: What Role Has the Muslim Population Played in Shaping Indian Heritage?
The cultural contributions of the Muslim population in India are vast and multifaceted, influencing everything from cuisine to music. Indian cuisine, for example, owes much of its richness to Mughlai dishes like biryani, kebabs, and korma. These culinary traditions have become an integral part of Indian gastronomy, enjoyed by people of all backgrounds.
Music and art are other domains where the Muslim community has left an indelible mark. The development of Hindustani classical music, for instance, owes much to Muslim patrons and musicians. Renowned artists like Amir Khusrau and Tansen played pivotal roles in shaping this genre. Similarly, Urdu poetry, with its themes of love, mysticism, and social justice, continues to captivate audiences worldwide.
Architectural marvels like the Taj Mahal and Jama Masjid are enduring symbols of the Muslim population’s artistic legacy. These structures not only reflect Islamic architectural principles but also incorporate local Indian elements, creating a unique fusion of styles. Such contributions underscore the community’s role in enriching India’s cultural heritage.
Economic Impact: How Does the Muslim Population Contribute to India’s Economy?
The Muslim population in India plays a vital role in the country’s economic landscape, contributing through entrepreneurship, labor, and innovation. Despite facing socio-economic challenges, many Muslims have excelled in business, particularly in sectors like textiles, handicrafts, and food processing. Cities like Mumbai, Hyderabad, and Kolkata are home to thriving Muslim-owned enterprises that generate employment and drive economic growth.
Here are some notable contributions:
- Textile Industry: Muslims dominate the handloom and embroidery sectors, producing exquisite fabrics like Chikankari and Banarasi silk.
- Food Industry: From street food vendors to restaurant chains, Muslims have popularized dishes like biryani and kebabs, contributing to India’s culinary tourism.
- Artisanal Crafts: Traditional crafts like zardozi, block printing, and pottery are often associated with Muslim artisans, preserving India’s artisanal heritage.
Despite these achievements, the Muslim population faces significant economic disparities. Studies indicate lower literacy rates and limited access to formal education and employment opportunities. Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensuring the community’s full participation in India’s economic progress.
What Challenges Does the Muslim Population in India Face Today?
The Muslim population in India grapples with a range of socio-economic and political challenges that hinder their progress. One of the most pressing issues is educational disparity. Many Muslim children lack access to quality education, leading to lower literacy rates and limited career opportunities. This educational gap perpetuates cycles of poverty and marginalization.
Political representation is another area of concern. While Muslims constitute a significant portion of the population, their representation in legislative bodies remains disproportionately low. This underrepresentation often results in policies that fail to address the community’s specific needs. Additionally, communal tensions and stereotypes further exacerbate their marginalization.
Despite these challenges, the Muslim population in India continues to demonstrate resilience. Community-led initiatives, such as educational trusts and skill development programs, are empowering the younger generation to overcome these barriers. By fostering inclusivity and addressing systemic issues, India can unlock the full potential of its Muslim population.
Political Influence: How Does the Muslim Vote Shape Indian Democracy?
The Muslim vote is a significant factor in Indian elections, influencing the outcome in key constituencies. Given their substantial population, Muslims often hold the balance of power in states like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal. Political parties recognize this influence and tailor their campaigns to address issues relevant to the Muslim population.
However, the Muslim population’s political engagement is not without challenges. Communal polarization and identity politics often overshadow their concerns, leading to tokenistic representation. Moreover, the rise of majoritarian ideologies has raised questions about the community’s safety and rights. Despite these hurdles, Muslims continue to participate actively in the democratic process, advocating for equality and justice.
Social Initiatives: Are There Efforts to Empower the Muslim Community in India?
Empowering the Muslim population in India requires concerted efforts from both the government and civil society. Various initiatives have been launched to address educational and economic disparities within the community. For instance, the Sachar Committee Report (2006) highlighted the socio-economic challenges faced by Muslims and recommended targeted interventions.
Some notable initiatives include:
- Educational Scholarships: Programs like the Maulana Azad National Fellowship provide financial assistance to Muslim students pursuing higher education.
- Skill Development: Vocational training centers aim to equip Muslim youth with employable skills.
- Women’s Empowerment: Organizations like Self-Employed Women’s Association (SEWA) focus on empowering Muslim women through microfinance and entrepreneurship.
While these efforts are commendable, sustained commitment is needed to bridge the gap between policy and implementation. Collaborative action involving government agencies, NGOs, and the private sector can create a more inclusive environment for the Muslim population in India.
What Does the Future Hold for the Muslim Population in India?
The future of the Muslim population in India hinges on addressing existing challenges while leveraging their strengths. Education, economic empowerment, and political representation will be critical to ensuring their equitable participation in the nation’s progress. As India continues to evolve, the Muslim community’s contributions will remain vital to its cultural, economic, and social fabric.
FAQs
What is the current population of Muslims in India?
As of the 2011 Census, the Muslim population in India is approximately 172 million, constituting about 14.2% of the total population. This number is expected to grow in the coming years.
How does the Muslim population in India contribute to the arts?
The Muslim population has significantly influenced Indian art, particularly in music, poetry, and architecture. Contributions include Hindustani classical music, Urdu literature, and iconic structures like the Taj Mahal.
What are the main challenges faced by Muslims in India?
Key challenges include educational disparities, limited economic opportunities, political underrepresentation, and communal tensions. Addressing these issues is crucial for fostering inclusivity and equality.
In conclusion, the Muslim population in India is a vibrant and integral part of the nation’s identity. Their contributions to culture, economy, and society underscore their importance in shaping India’s future. By addressing existing challenges and promoting inclusivity, India can ensure that this diverse community continues to thrive and contribute to the nation’s progress.
For more information on the Muslim population in India, you can explore resources like the Census of India.