Understanding the molar mass of CoCl2 (Cobalt(II) Chloride) is essential for students, chemists, and researchers alike. This compound plays a significant role in various chemical reactions and industrial applications. Whether you're studying chemistry, working in a laboratory, or simply curious about how compounds like CoCl2 function, knowing its molar mass is a foundational aspect of chemical calculations. In this article, we will delve into the concept of molar mass, how it is calculated, and why it matters in the context of Cobalt(II) Chloride.
CoCl2 is a compound composed of one cobalt atom and two chlorine atoms. Its molar mass is a crucial factor in stoichiometry, which is the calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions. Understanding the molar mass of CoCl2 allows scientists and students to determine how much of the compound is needed for specific experiments or processes. This knowledge is not only important for academic purposes but also for real-world applications, such as water treatment, pigment production, and catalyst preparation.
In this article, we will explore the molar mass of CoCl2 in detail, covering its calculation, significance, and applications. We will also discuss its physical and chemical properties, safety considerations, and how it is utilized in various industries. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of CoCl2 molar mass and its importance in chemistry and beyond.
Read also:Jehovah Rapha What Does Jehovah Rapha Mean And Why Is It Important
Table of Contents
What is CoCl2?
CoCl2, or Cobalt(II) Chloride, is an inorganic compound that exists as a blue crystalline solid in its anhydrous form and as a pink solid in its hydrated form (CoCl2·6H2O). It is widely used in laboratories and industries due to its unique properties. Cobalt(II) Chloride is known for its ability to change color based on its hydration state, making it a popular indicator in certain chemical processes.
The compound is composed of one cobalt (Co) atom and two chlorine (Cl) atoms. The cobalt atom has an oxidation state of +2, which is why it is referred to as Cobalt(II) Chloride. This compound is highly soluble in water and ethanol, making it versatile for various applications. Its ability to absorb moisture from the air (hygroscopic nature) also adds to its utility in specific industrial processes.
Understanding Molar Mass: The Basics
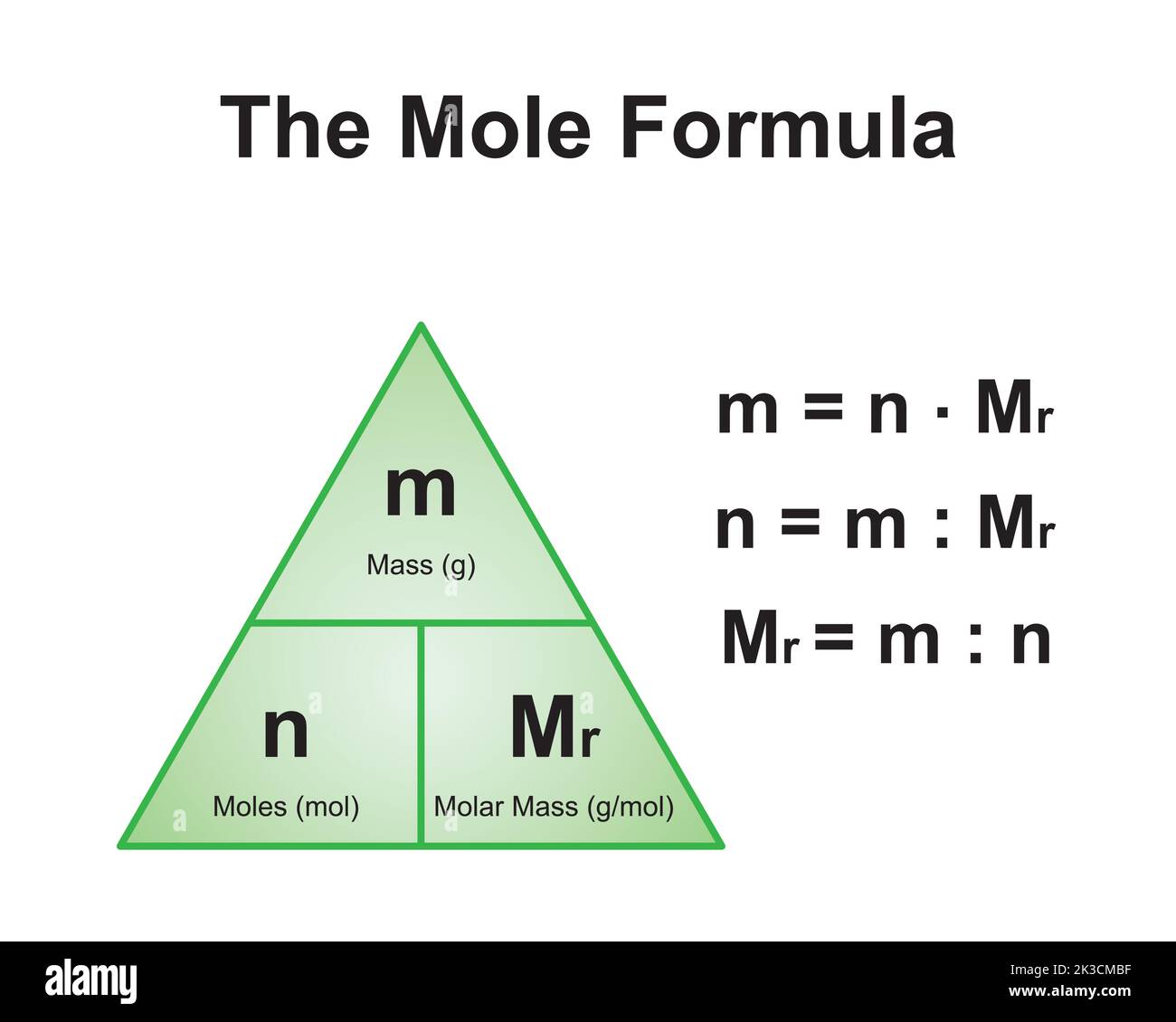
Molar mass is a fundamental concept in chemistry that refers to the mass of one mole of a substance. One mole is defined as 6.022 x 10^23 particles (Avogadro's number), which can be atoms, molecules, or formula units. The molar mass is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol) and is calculated by summing the atomic masses of all the atoms in a chemical formula.
For compounds like CoCl2, the molar mass is determined by adding the atomic masses of cobalt and chlorine. The atomic mass of cobalt is approximately 58.93 g/mol, while chlorine has an atomic mass of 35.45 g/mol. By understanding molar mass, chemists can accurately measure and predict the behavior of substances in chemical reactions.
How to Calculate CoCl2 Molar Mass
Calculating the molar mass of CoCl2 involves a straightforward process. First, identify the atomic masses of the elements in the compound. The atomic mass of cobalt (Co) is approximately 58.93 g/mol, and the atomic mass of chlorine (Cl) is approximately 35.45 g/mol. Since there are two chlorine atoms in CoCl2, the total mass of chlorine is 35.45 x 2 = 70.90 g/mol.
Next, add the atomic masses of cobalt and chlorine to determine the total molar mass of CoCl2. The calculation is as follows:
Read also:Is Itadori A Special Grade Unveiling The Truth Behind The Hype
- Cobalt (Co): 58.93 g/mol
- Chlorine (Cl): 70.90 g/mol
- Total Molar Mass: 58.93 + 70.90 = 129.83 g/mol
Thus, the molar mass of CoCl2 is 129.83 g/mol.
Step-by-Step Calculation Process
Here is a step-by-step guide to calculating the molar mass of CoCl2:
- Identify the chemical formula of the compound (CoCl2).
- Find the atomic masses of cobalt and chlorine from the periodic table.
- Multiply the atomic mass of chlorine by 2, as there are two chlorine atoms in the formula.
- Add the atomic mass of cobalt to the total mass of chlorine.
- Express the result in grams per mole (g/mol).
Applications of CoCl2 in Various Industries
Cobalt(II) Chloride has a wide range of applications across different industries. One of its primary uses is as a catalyst in organic synthesis, particularly in the production of hydrocarbons and polymers. It is also employed in the formulation of pigments and dyes, where its vibrant color properties are highly valued.
In the field of water treatment, CoCl2 is used as a moisture indicator and desiccant. Its ability to change color when exposed to moisture makes it an effective tool for monitoring humidity levels. Additionally, CoCl2 is utilized in the production of vitamin B12, a crucial nutrient for human health.
Chemical Properties of CoCl2
CoCl2 exhibits several notable chemical properties. It is highly soluble in water and ethanol, forming a pink solution in its hydrated form. When heated, the compound loses water molecules, transitioning from a pink solid to a blue anhydrous form. This color change is reversible, making CoCl2 a useful indicator in certain chemical reactions.
CoCl2 also reacts with ammonia to form complex compounds, such as hexamminecobalt(III) chloride. These complexes are studied extensively in coordination chemistry due to their unique structures and properties.
Physical Properties of CoCl2
The physical properties of CoCl2 include its crystalline structure, color, and solubility. In its anhydrous form, CoCl2 appears as a blue crystalline solid, while its hydrated form (CoCl2·6H2O) is pink. The compound has a melting point of approximately 735°C and a boiling point of 1049°C.
CoCl2 is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air. This property makes it useful in applications where moisture control is critical, such as in desiccants and humidity indicators.
Safety Precautions When Handling CoCl2
While CoCl2 is a valuable compound, it requires careful handling due to its potential health hazards. It is classified as a toxic substance, and prolonged exposure can cause skin and respiratory irritation. Ingestion or inhalation of CoCl2 dust should be avoided, as it may lead to adverse health effects.
When working with CoCl2, it is essential to use personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and a lab coat. Proper ventilation should also be ensured to minimize exposure to fumes or dust. Additionally, CoCl2 should be stored in a cool, dry place away from incompatible substances, such as strong acids or bases.
Real-World Uses of CoCl2
CoCl2 finds applications in various real-world scenarios. In the laboratory, it is used as a reagent for detecting the presence of water in solvents. Its color-changing property makes it an effective visual indicator for moisture levels.
In the agricultural industry, CoCl2 is used as a micronutrient in fertilizers to provide cobalt, an essential element for plant growth. It is also utilized in the production of catalysts for the petroleum industry, where it enhances the efficiency of chemical reactions.
Common Misconceptions About CoCl2 Molar Mass
One common misconception about CoCl2 molar mass is that it remains constant regardless of its hydration state. While the molar mass of anhydrous CoCl2 is 129.83 g/mol, the hydrated form (CoCl2·6H2O) has a higher molar mass due to the inclusion of water molecules. The molar mass of CoCl2·6H2O is approximately 237.93 g/mol.
Another misconception is that molar mass is the same as molecular weight. While the two terms are related, molar mass specifically refers to the mass of one mole of a substance, whereas molecular weight is the sum of the atomic weights of all atoms in a molecule.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the molar mass of CoCl2 is crucial for anyone involved in chemistry, whether as a student, researcher, or professional. The molar mass of CoCl2, calculated to be 129.83 g/mol, is a key factor in stoichiometric calculations and various industrial applications. From its role as a catalyst to its use in moisture detection, CoCl2 demonstrates versatility and importance in multiple fields.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of CoCl2 molar mass and its significance. If you found this guide helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from this information. Additionally, feel free to leave a comment or explore more articles on our site to deepen your knowledge of chemistry and related topics.